The most practical guide to date by the openAI has been released, and it is a clear roadmap on how to create and comprehend AI agents. This guide has not been big news, but it redefines our cognition of intelligent automation.
In case you were ever curious about what exactly an AI agent is or how to make one, the plain-English version is as follows.
An AI agent is not any other chatbot. It is a system capable of thinking, making decisions and acting on them without having to be instructed on each and every step.
Consider it a self-driven digital assistant: it has a vision, makes choices and does the right actions with the help of appropriate tools.
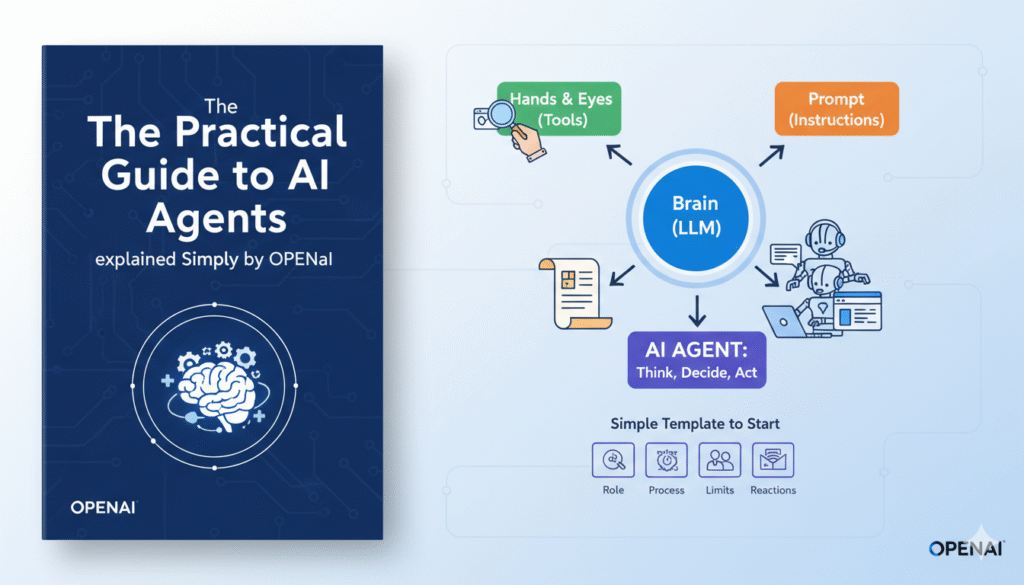
The 3 Core Building Blocks
Any AI agent, even the most sophisticated one, is composed of three fundamental elements:
The decision-maker is the Brain (LLM). The giant language model, such as GPT-5, understands instructions and determines the next course of action.
The Hands and Eyes tools (Tools): These help the agent to browse the web, view files or work with applications. Their link to the intelligence of the AI is to the actual action.
The Prompt (Instructions) – This is what behavior is. It informs the agent of its aims, voice and constraints – influencing its way of thinking and acting.
These three components put together make up a system that does not merely provide answers to questions, it works.
How to Build Your Own AI Agent
Development of an AI agent is easier than ever. Here’s the process:
Use GPT-5 as the brain of your agent.
Add utilities like file search, accessing the browser or automation of the web.
Write instructions that are clear and specific and remove ambiguity.
The idea is to get your agent to be able to think on his/her own, but within prescribed guidelines and limitations.
A Simple Template to Start
The guide of open AI recommends identifying four things:
Role- Who or what the agent represents.
Process – Its sequence or route of operation.
Limits – What it is not capable of doing or in what case to seek assistance.
Reactions – How it is to react when in doubt.
(And no, it isn’t sufficient to tell it as it would help)
Real-World Example
Consider an AI agent that does sales and customer support, i.e. follow-ups on leads, frequently asked questions, and data logging all with minimum code.
That’s not futuristic. It’s available now.